Find Nearest Features
Purpose
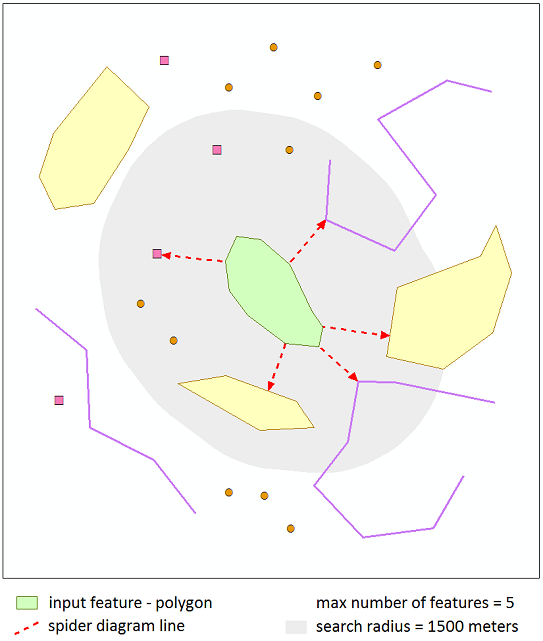
The tool allows finding nearest features from the same or other near datasets, calculating distances and other proximity information. You can add calculated parameters to the input dataset or new standalone table, or create Spider diagram lines between nearest features.
Description
The Find Nearest Features tool finds the nearest features in specified search radius and calculates the proximity attributes. You can select Planar method or Geodesic to calculate distances between input and candidate features for finding the nearest features.
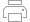
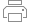
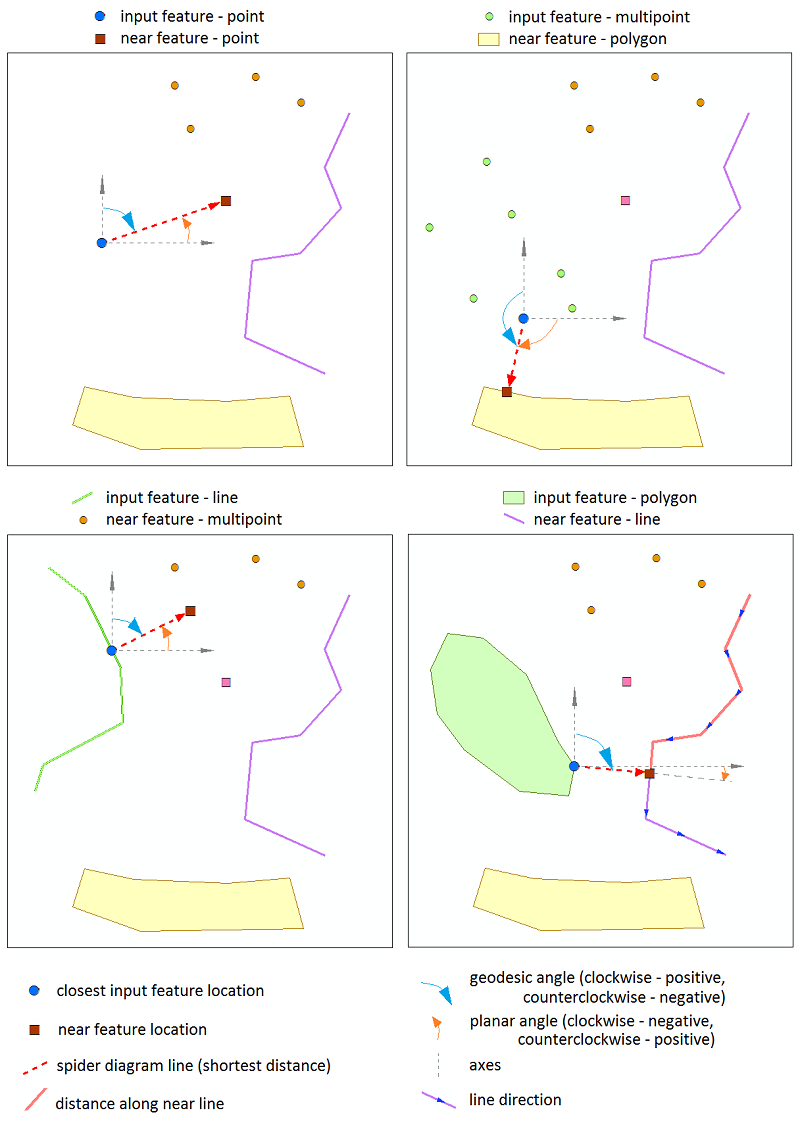
Both the input and candidate features can be points, multipoints, lines, and polygons. At that, it is possible to search for nearest features in a few candidates.
Output fields with calculated proximity parameters can be added to the input dataset, a new table, or a new feature class with created Spider diagram lines between input and near features.
Adding proximity parameters to the input dataset, the nearest feature only can be found for each input feature. Creating Spider diagram lines or new table as output, you can specify maximum number of the nearest features and find more than one near feature for each input feature.
Note
Calculating distances, Z coordinates are not taken into account. Output feature class with spider diagram lines won't have Z coordinate.
Usage
-
Select the "Find Nearest Features" tool from the XTools Pro Overlay tools.
-
Select input features.
-
Select datasets with the candidate features, input dataset can be selected here as well. Near features can be found for either all or only selected features in both input and candidate datasets.
-
Select if calculated proximity parameters should be added to the input dataset or a new table, or a new Spider diagram feature class should be created.
-
Select to use either geodesic or planar distances.
-
Select proximity attributes and optionally specify/change field names.
-
Specify maximum number of the nearest features (if creating Spider diagram or new table as output).
-
Specify search radius and select search radius units.
-
Press Run to find nearest features.
Selecting proximity parameters
The following proximity parameters can be calculated for the nearest features:
-
Distance
- the shortest distance between input and near features (Geodesic or Planar). -
Distance along line
- the distance (Geodesic or Planar) from the first point of the near line feature to the projection of the closest input feature location onto this line (available for line candidate features). -
Near feature ID
- ID of the candidate feature containing the nearest location to the input feature. -
Dataset path
- the path to candidate feature class containing near feature. -
X coordinate
- X coordinate of the near feature location. -
Y coordinate
- Y coordinate of the near feature location. -
Angle
- the angle in degrees between a line, connecting input feature and near feature location in the shortest distance, and X-axis (0° - East, 90° - North, -90° - South, used with selected Planar distances) or North (0° - North, 90° - East, -90° - West, used with selected Geodesic distances). -
Line side
- the side of near line feature (by its direction) where there is the closest input feature location (0 - left side, 1 - right side, available for line candidate features). -
Input feature ID
- the input feature ID which the near feature has been found for (available if creating Spider diagram or new table as output). -
Input X coordinate
- X coordinate of the closest input feature location to the near feature (available if creating Spider diagram or new table as output). -
Input Y coordinate
- Y coordinate of the closest input feature location to the near feature (available if creating Spider diagram or new table as output).
Notes
-
If the nearest feature hasn't been found for the input feature (adding output to the input dataset), Dataset path parameter will be empty, Angle will be "0", other parameters will be "-1".
-
Processing only selected features in both the input layer and candidate layers is supported.
-
For X, Y coordinates and Input X, Y coordinates parameters, units depend on the selected method to calculate distances (Geodesic or Planar). If Planar is selected, coordinates will be in the linear units of the input spatial reference. If Geodesic is selected, coordinates will be in the units of the geographic coordinate system associated with the input spatial reference.
-
If creating Spider diagram or new table as output, it is recommended to select Input feature ID parameter to match output records with input features later.
Using planar or geodesic distances
The nearest features can be found using Planar or Geodesic distances. Adding distances to the attribute table there is an option to select distance units.
Notes
-
Selecting Planar distances, for input dataset in geographic coordinate system you cannot select units (distances will be added in degrees).
-
For input or candidate dataset in unknown coordinate system only Planar distances are available to be used (distances will be added in unknown units).
-
It is recommended to use the Geodesic method for datasets in geographic coordinate systems and datasets covering large geographic areas.
Specifying optional parameters
-
Max number of features
You can specify maximum number of the nearest features to be found for each input feature.
Parameter can be only positive or empty. If it is empty, selected proximity parameters of all candidate features (in specified search radius) can be added to the output table.
Parameter is available if creating Spider diagram or new table as output.
Note
If maximum number of the nearest features is not specified, the output table may be huge and may take some time to create.
-
Search radius
The nearest features will be found in the specified radius.
Parameter can be zero, positive or empty. If it is empty, the nearest features will be found among all the candidate features. If search radius is zero, only candidate features with at least one point contained in input feature are taken into account.
You can select search radius units. For input dataset in Unknown coordinate system, specified radius units is considered as Unknown units.