Shapes to Centroids
Purpose
Input features: 

Output features: 
The tool creates a new point feature class from the centroids of the shapes in the input features.
Description
Features of any geometry type are supported for converting to centroids. Points and any other features can be grouped by one or a few attribute fields. Centroids will be created for groups of features in this case. For groups of features you can select to weight centroids by an attribute.
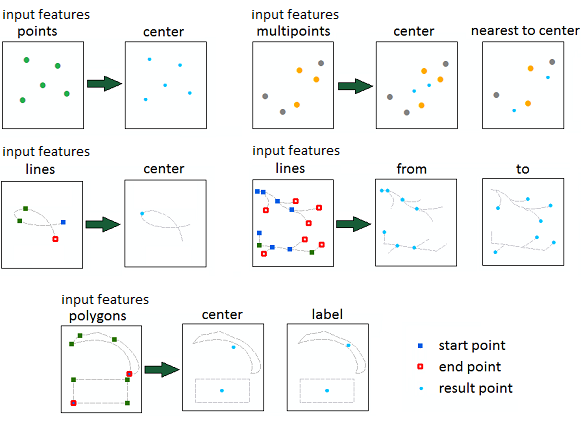
The following centroid locations are available:
-
Center - all points (for points), centroids (for multipoints, polygons or grouped features) or midpoints (for lines).
-
Nearest to center - the nearest real point to the feature centroid (for multipoints only).
-
From - start feature points (for lines only).
-
To - end feature points (for lines only).
-
Label - feature label points (for polygons only). Label points are always placed within features.
Resulting centroids feature class can be stored in a new shapefile or geodatabase feature class. Attributes from the source layer are transferred to the output points layer (for centroids made for groups of features only the group field is kept).
Notes:
-
Numeric fields with weights are supported. At that only positive values are taken into account, features with negative, zero or "Null" weights are ignored.

-
Output centroids for input 3D features will be Point Z. But centroids will be calculated using only X and Y coordinates of input features. Z coordinate of output centroids will be "0".
Usage
-
Select the "Shapes to Centroids" tool from the XTools Pro Conversions tools.
-
Select the input features that you wish to convert to centroids.
-
Specify the name and location of the output centroids feature class.
-
Select one or a few fields to group input features if you wish to create centroids for groups of features.
-
Select input field to weight centroids by (creating centroids for groups of features).
-
Select centroid location.
-
Press Run to convert shapes to centroids.
Examples
Examples of when the tool can be used:
-
Use it to represent two properties of the same shapefile at the same time. Use the input layer legend to represent the first property while the legend of the new centroid point layer will represent a second property using the transferred attributes.
-
Use it in special cases of spatial joins (shapefield to shapefield joins). Suppose you have two polygon shapefiles A and B. You want to transfer attributes of A to B. Of course, you could do something like an overlay, but sometimes this is undesirable. Also, there are no unique identifiers identical for two layers on which you could make a normal join. So how this task can be accomplished? Here is one of the approaches: create a centroid layer from B, then create a spatial join with A. Now the data from the polygons from A may be joined to the centroid shapefile (you cannot perform a spatial join in case when the data from points were transferred to polygons, because there might be more than one point inside one polygon). Since you have the unique identifiers from B in your centroid layer, you can now join the centroid layer to the layer table of B. Data transferred!